“The eyes are the window to the soul” 16th century proverb
The retina gives an unobstructed view of the human vascular.
Also, retinal imaging is important for diagnosing retina diseases.
Fundus camera:
Is a device for photographing the retina.

It is based on the indirect ophthalmoscopy principle, where the Observer’s eye is replaced with a camera.
So, A fundus camera or (retinal camera)
Is a specialized low power Microscope with an attached Camera designed to Photograph the interior surface of the Eye, including the Retina, Optic disc, Macula, and Posterior pole i.e. the Fundus (eye).
Optical principles:
The optical design of fundus cameras is based on the principle of monocular indirect ophthalmoscopy.
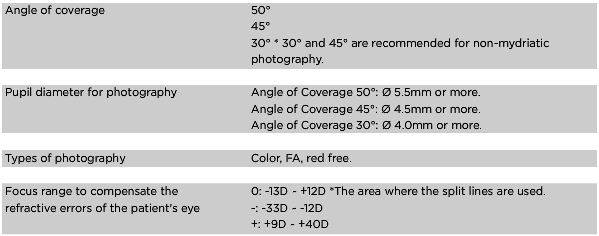
A fundus camera provides an upright, magnified view of the fundus. A typical camera views 30 to 50 degrees of retinal area, with a magnification of 2.5x, and allows some modification of this relationship through zoom or auxiliary lenses from 15 degrees which provides 5x magnification to 140 degrees with a wide angle lens which minifies the image by half. The optics of a fundus camera are similar to those of an indirect ophthalmoscope in that the observation and illumination systems follow dissimilar paths.

The observation light is focused via a series of lenses through a doughnut shaped aperture, which then passes through a central aperture to form an annulus, before passing through the camera objective lens and through the cornea onto the retina.The light reflected from the retina passes through the un-illuminated hole in the doughnut formed by the illumination system. As the light paths of the two systems are independent, there are minimal reflections of the light source captured in the formed image. The image forming rays continue towards the low powered telescopic eyepiece.
When the button is pressed to take a picture, a mirror interrupts the path of the illumination system allow the light from the flash bulb to pass into the eye. Simultaneously, a mirror falls in front of the observation telescope, which redirects the light onto the capturing medium, whether it is film or a digital Charge-coupled device.
Because of the eye’s tendency to Accommodation (eye) while looking though

a telescope, it is imperative that the exiting Vergence is parallel in order for an in focus image to be formed on the capturing medium.
Since the instruments are complex in design
and difficult to manufacture to clinical standards, only a few manufacturers exist:
Topcon,
Zeiss, Canon, Nidek, and
Kowa

Applications:
for fundus photography performing the following modes of examination:
1. Color, where the retina is illuminated by white light and examined in full color.

2. Red-free, where the imaging light is filtered to remove red colors, improving contrast of vessels and other structures.
 3. Angiography, where the vessels are brought into high contrast by intravenous injection of a fluorescent dye. The retina is illuminated with an excitation color which fluoresces light of another color where the dye is present. By filtering to exclude the excitation color and pass the fluorescent color, a very high-contrast image of the vessels is produced. Shooting a timed sequence of photographs of the progression of the dye into the vessels reveals the flow dynamics and related pathologies. Specific methods include sodium fluorescein angiography.
3. Angiography, where the vessels are brought into high contrast by intravenous injection of a fluorescent dye. The retina is illuminated with an excitation color which fluoresces light of another color where the dye is present. By filtering to exclude the excitation color and pass the fluorescent color, a very high-contrast image of the vessels is produced. Shooting a timed sequence of photographs of the progression of the dye into the vessels reveals the flow dynamics and related pathologies. Specific methods include sodium fluorescein angiography.
Pre-examination setting:
1. The examiner
Before attempting photography, must become very familiar with the camera through a training session and by learning the terminology of the camera operation Manual .
2. Examination room
- The room lights are dimmed so that only the lights of the camera and computer monitors remain on.
- The majority of the exam is performed in the dark.
3. The camera
- The camera is mounted on a motorized table for easy Height adjustment, and both the examiner and the SP have an adjustable stool to sit on
- Before each SP is photographed, the objective lens should be checked and cleaned if necessary.
- High humidity or temperatures must be avoided. Dusty conditions mean that the camera will need frequent cleaning.
- It its extremely important that camera lens be inspected and cleaned, if dirty, before each photograph. The retinal camera should remain covered when not in use and the lens should be capped after each SP photograph.
- A checklist itemizing procedures for preparing the camera at the start of each day is posted on the wall near the fundus camera.
- Technicians responsible for the fundus equipment should carefully follow the daily procedures.
4. The patient
- Photography begins with a complete explanation of the procedure to the SP by the examiner.
- It is important to reassure the SP that no retinal damage is caused by this procedure.
- The camera flash is bright and the SP should know when to expect a flash. Since pictures will include the macula (area of central vision), it is normal for the SP to experience a blue or red tint to vision immediately following the flash.
- This totally disappears within two to five minutes. No dilation drops are used for this examination, In non mydriatic procedure and the eyes will not be touched.
BENEFITS OF DIGITAL PHOTOGRAPHY:
- Instant knowledge of image quality
- Networking of images (a must)
- Reduction in administration time
- No film / development costs
- Easy export for presentations / e.mail
- Instantly available for viewing
- Comparison over time on screen
- Digital image manipulation tools
- Linkage to Electronic Patient Records
- Diagnostic Database
NIDEK (Non-Mydriatic) Auto Fundus Camera
NIDEK delivers the innovative non-mydriatic digital fundus camera that integrates every function required for easy retinal screening. Customized built-in functions of the NIDEK AFC-230/210 improve the quality and efficiency of medical examinations.
It has a screen connection.
Features
- Innovative and unique Auto Focus and Auto 3D* Tracking.
*AFC-230 Only - High Quality Retinal Imaging
Integrating the innovative imaging optical system, this technologically advanced AFC-230/210 realizes digital fundus imaging of high resolution and fine gradation. - Accurate Anterior Eye Observation before Photography
The AFC230/-210 integrates the 5.7-inch TFT LCD (640 x 480) monitor in addition to the special optic system. - Unique Blink Control
With the automatic blink detection, the AFC-230/210 automatically stops the photography when the patient blinks. - Anterior Eye Photography Mode
- Smaller Pupil Diameter Mode
In addition to the regular minimum Pupil Diameter ø4.0 mm, the AFC-230/210 is also highly capable of detecting a smaller Pupil Diameter Minimum 3.7 mm. - Stereo Mode*
Stereo fundus photography is also possible.
*Requires stereo viewer (optional).
fundus camera


| *3 modes with one-touch switch ( nonmydriatic / mydriatic / fluorescein ). |
| *Mydriatic color and fluorescein photography can now be aligned through the LCD observation monitor. |
| *Built-in internal fixation target for optic nerve head photography. |
| Easy alignment and focusing adjustment with the LCD observation monitor. | |
| Operationally focused, darkroom adapted navigation panel. | |
| Clear viewfinder with a Long Eye Relief design. | |
| Simple focusing with the point matching method. | |
| Electric insertion of the fluorescein filter. |
|
| Newly developed video adapter enables you to take both standard color photography and fluorescein angiography by high resolution Nikon* digital SLR camera. | |
| All taken images are transferred the VK-2 imaging system automatically. |
|
Retinal Camera
Canon CX-1 Retinal Camera
The CX-1 is a MYD and Non-MYD hybrid digital retinal camera. It is extremely versatile with its 5 photography modes; colour. FAG, red free, cobalt and FAF (Fundus Auto Fluorescence). Making it ideal for screening and the diagnosis of the main eyes diseases.
| |
Features | |
| |
| Canon’s CX-1 is a compact and portable hybrid retinal camera that combines both Mydriatic and Non-Mydriatic Modes, and switches between the two with a simple touch of a button. | |
Hybrid camera : Canon’s CX-1 is a compact and portable hybrid retinal camera that combines both Mydriatic and Non-Mydriatic Modes, As well as saving on equipment investment, this function also means that the examiners using the equipment can screen for more than one disease, e.g. AMD (Age-related Macular Degeneration), Glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy, with the same unit. This saves time and removes the need for repeat appointments. 5 Photography Modes With the CX-1 following photography modes are available; Color, Red-free, Cobalt, Fluorescein Angiography and Fundus Autofluorescence (FAF) Alignment and observation with the CX-1 can be done through the viewfinder or by the large EOS LCD screen FAF (Fundus Auto Fluorescence) Detecting Auto fluorescence of the retina is an important indication of the retina’s health. With the CX-1 it is possible to take FAF (Fundus Auto fluorescence) images, even in Non-Mydriatic mode. Use of EOS Technology Canon’s own EOS camera technology, with its renowned image processing capabilities, is adapted exclusively for medical use in the CX-1 to provide optimal retinal imaging in a compact and convenient system. The single onboard 15.1 MegaPixel digital camera handles five different photography modes with ease, including non-mydriatic FAF photography, allowing EOS imaging technology to benefit all retinal images from the CX-1. Enhanced stereo photography function Easy capture for stereo view, by using the stereo guide marks on EOS LCD in the non-mydriatic mode, or stereo unit (option) a stereo pair can be created and managed very simply Bundled Retinal Imaging Control Software Bundled Retinal Imaging Control Software (RICS) for full camera control and image optimalization. The software has extensive diagnostic tools for optimized workflow and patient management; e.g. Cup/Disc ratio calculation, compare studies, RGB channel display, stereo viewing Open connectivity and DICOM compliant The CX-1 with RICS has open connectivity with existing networks and is fully DICOM compliant.
different models:
High Resolution 15.1 Megapixel Retinal camera systems are available!
Canon CR2 Non Mydriatic Retinal Camera with new Portable Design New Canon CX1 Myd and Non Myd Retinal camera with patient friendly Non Myd FA plus Color, RF, Cobalt, FA and FAF (RPE Fundus Photo) imaging Ease of use for Retinal Screening, Glaucoma Stereo Imaging and Anterior Segment imaging of Cornea, Iris, Pupil and Lens Canon Capture software with DICOM, JPEG or TIFF File output to EMR's and PACS Canon CR2 RICS Capture software enhances clinical workflow efficiency by providing R, G, B, Red-Free |
retinal cameras
TRC-NW7SF MK II
Description:
The TRC-NW7SF offers you the versatility of dilated and undilated retinal imaging in both black & white and colour modes. In the non-mydriatic mode, the TRC-NW7SF can make colour, red-free and fluorescein images. In the mydriatic mode, it can also shoot ICG live and still images.
For ease of alignment and focusing, 6.4 inches colored monitor is available. This monitor can be used for capturing still and live images and with its ability to be angled a full 90 degrees side to side, allows the operator to concentrate on getting the patient perfectly positioned. TRC-NW7SF has a touch screen control panel for simple changes in procedures. Each procedure has its own pre-setting and background colour. The touch screen incorporates smart features such as small pupil mode and aperture adjustment for an enhanced depth of field. The swing and tilt mechanism allows viewing of peripheral segments without moving the patient’s head or fixation.
KEY FEATURES
-The ultimate all-in-one OCT.
-High resolution OCT.
-High resolution colour fundus image.
-High resolution FA & FAF images.
-Intuitive workflow.
-Normative database.
-Glaucoma module.
-network support (Full).